Question 1: Define and explain the following:
(1) Equal Vectors (2) Negative of a vector (3) Null or zero Vectors
(4) Unit Vector (5) Position Vector
ANSWER
(1) Equal vectors
Two or more than two vectors are said to be equal if they have same magnitude and same direction.
(2) Negative of a vector
Negative of a vector is defined as a vector of the same magnitude but in the reverse direction.
(3) Null or zero vector
Null vector is a vector having zero magnitude and arbitrary direction.
(4) Unit vector
Vector whose magnitude equals one is called a unit vector.
Unit vector is denoted by  and read as A hat or A cap. Any vector can be written as
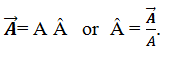
A common notation for denoting unit vector along the position vector is ȓ and normal to a specific surface is n̑.
(5) Position vector
It is defined as the vector which determines the position of a point in space or in a plane with respect to the origin or some other reference point.
It is represented by a straight line drawn in such a way that its tail coincides with the origin and the tip with the position of the point P.
In Cartesian plane the point P(x, y) from the origin O is given by,
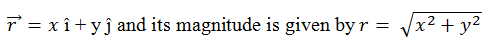
While in three dimensional space,
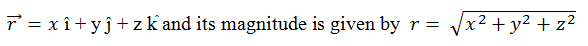

Pingback:vectors-and-equilibrium-addition-and-subtraction-of-vectors-condition-of-equilibrium – msa