Question 6: What is wheat stone bridge? Explain with diagram the balancing, the principle and the working of this bridge.
ANSWER
Wheatstone Bridge
It is one of the most convenient, precise and widely used instrument for measuring the unknown resistance.
This bridge was first proposed by an English telegraph engineer, Charles Wheatstone. It consists of a battery, Galvanometer and two fixed resistances R1 and R2 and one variable resistance R3 and the unknown resistance Rx which is to be found. The schematic diagram is shown below.
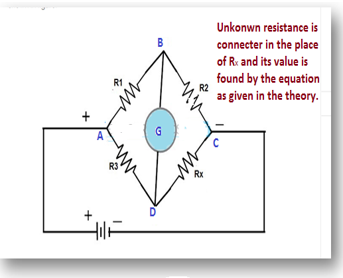
ABC and ADC are the two branches and the galvanometer circuit is the bridge across them. The battery is connected between points A and C and the galvanometer between B and D.
Balancing Principle and working theory
The principle of Wheatstone bridge is that if R1/R2 = R3/Rx, then the bridge will be in balance conditions and no current will pass through the galvanometer.
In the given circuit unequal currents will flow between the two branches, depending upon the resistances of the branch resistors. The galvanometer will show a deflection. However, adjusting the variable resistance R3, the current in the galvanometer can be made zero. At this stage, the potential difference between A and B will be identical as that of potential difference between A and D. Therefore, points B and D will be at same potential and hence no current will be flowing through the galvanometer. Similarly, the potential difference between C and D is identical as Potential difference between C and B.
Suppose I1 is the current flowing in resistors R1 and R2 and I2 is the current flowing in R3 and Rx, then, under such balanced conditions,
I1R1 = I2R3 and I1R2 = I2Rx
Now dividing the second equation by the first one;
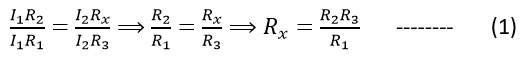
Thus the unknown resistance can be calculated.
This equation also implies that, R1/R2 = R3/Rx which verifies the principle of the galvanometer.
Equation (1) can be used to find the unknown resistance RX when it is connected in the circuit in the proper place.

Pingback:Comprehensive Questions, Current Electricity … msa – msa
Pingback:potentiometer-its-principle-construction-and-working – msa
Pingback:construction-of-rheostat-and-its-uses – msa