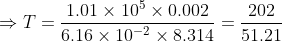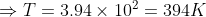(a): Given: Temperature, T = 20°C = 273 + 20 = 293 K Pressure, P = 1.50 × 105 Pa
Volume, V = 1.00 L = 0.001 m3
Required: Number of moles, n of the gas
Formula: The general gas law is, PV = nRT
Put values in the formula,
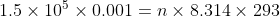
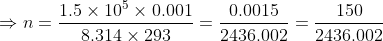
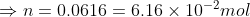
(b): Pressure = atmospheric pressure = 1.01 × 105 Pa
Volume = 2 × 0.001 = 0.002 m3
Required: Temperature T
Formula: PV = nRt
Put values in the formula, 1.01 × 105 × 0.002 = 6.61 × 10-2 × 8.314 × T