Question 4: What are X-rays? Give an account of the properties and uses of X-rays.
ANSWER
X-rays are high power penetrating radiations which are emitted from metal surface due to bombardment of highly energetic electrons.
Characteristic X-rays
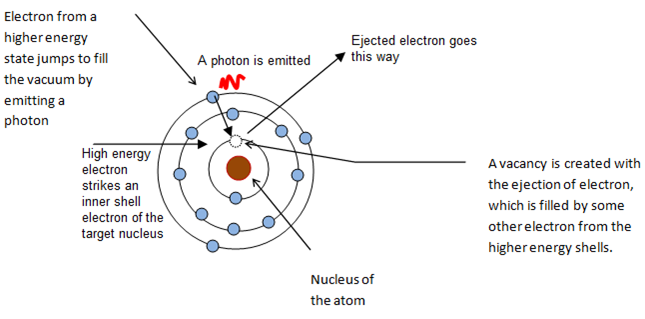
A high-energy electron, accelerated under several thousand electron volts, collide with inner shell electron of the target metal, it is knocked out from the atom. A vacancy (emptiness) is created there. Electron from a high-energy shell jumps down to fill the vacancy. As the jumping electron possesses more energy, the extra energy is emitted as X-ray photon. Such X-rays consists of specific wavelengths and are called characteristic X-rays.
A high-energy electron, accelerated under several thousand electron volts, collide with inner shell electron of the target metal, it is knocked out from the atom. A vacancy (emptiness) is created there. Electron from a high-energy shell jumps down to fill the vacancy. As the jumping electron possesses more energy, the extra energy is emitted as X-ray photon. Such X-rays consists of specific wavelengths and are called characteristic X-rays.
– For transition from L shell to K shell is called Kα characteristic X-rays.
– For transition from M shell to K shell is called Kβ characteristic X-rays.
– For transition from N shell to K shell is called Kγ characteristic X-rays.
We suggest you also see this article on x-rays in Urdu.
Continuous X-rays
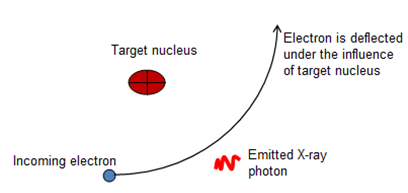
Let an electron is traveling towards a target nucleus in an X-rays tube. There are Coulomb forces (electrostatic forces) between this electron and the orbital electrons of the target nucleus as well as the nucleus itself. The charge on the nucleus is concentrated and very strong. This force accelerates the bombarding electron on its way. According to classical theory of electromagnetism, the accelerated electron emits braking radiations. This braking radiation is continuous and called continuous X-rays. This radiation appears in the form of photon of energy. Therefore, the incident electron must lose energy.
Let the incident electron is accelerated through a potential difference V, then its energy is eV. Suppose all this energy is transformed into the energy of photon. Then
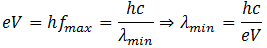
(Note that when frequency is maximum the corresponding wavelength is minimum)
However, all radiations would not have the maximum energy or minimum wavelength. It is because all the electrons are not stopped in a single collision. This results in the production of continuous spectrum.
Properties of X-rays
X-rays have the following properties.
- X-rays can be diffracted.
- They penetrate into the solid substances.
- When they pass through the solid, liquid or gas, they ionize the atoms.
- They cast shadows of the obstacles placed in their path.
- They are not refracted when passing from one medium to another.
- They cause fluorescence in many substances.
- They affect photographic plate.
Uses of X-rays
X-rays have scientific, industrial and medical uses.
- Scientific use: X-rays are used in crystallography in scientific work. The Laue diffraction pattern can be used to determine the internal structure of the crystals. By diffraction of X-rays the spacing and location of atoms in a crystal can be determined.
- Industrial uses of X-rays: X-rays penetrate in the material. In industries, X-rays are used to detect defects in the metallic structure.
- Medical uses of X-rays: X-rays are used for the detection of fractures in the bones. X-rays are also used in medicines for the treatment of diseases like cancer.

Pingback:lasers-its-principle-operation-and-uses – msa
Pingback:excitation-energy-ionization-energy-normal-state-excited-state – msa
Pingback:long-questions-ch19-p12 – msa