Question 8: Explain the phenomenon of electric polarization. Discuss how the phenomenon of polarization account for the increase in the capacitance of a capacitor when instead of air, dielectric is inserted between the plates?
ANSWER
Electric Polarization
Suppose a dielectric (material medium between the plates) is inserted between the plates of a capacitor with charges +Q and -Q as shown in the figure. Electrons in the atoms of dielectric are attracted by the positive plate and the nuclei by the negative plate.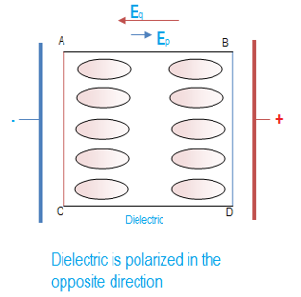 Electrons in the dielectric are not free and cannot leave the atoms which they are attached to; but they can undergo slight displacements towards the positive plate. The nuclei undergo similar displacements towards the negative plate. The effect of these minute displacements throughout the dielectric is that the dielectric is polarized. The electrical centers of the charges of electrons and nuclei don’t coincide. As a consequence, one surface of the dielectric acquires a positive charge and the other negative. The charge on the dielectric faces is called induced polarization charges. The electric field caused by the polarized charges is opposite to the applied field. Thus the resultant field due to the presence of the insulator is less intense than the case when there is only empty space between the plates. This property of dielectric is called permittivity, ε. For empty space the permittivity is ε0. The relative permittivity is
Electrons in the dielectric are not free and cannot leave the atoms which they are attached to; but they can undergo slight displacements towards the positive plate. The nuclei undergo similar displacements towards the negative plate. The effect of these minute displacements throughout the dielectric is that the dielectric is polarized. The electrical centers of the charges of electrons and nuclei don’t coincide. As a consequence, one surface of the dielectric acquires a positive charge and the other negative. The charge on the dielectric faces is called induced polarization charges. The electric field caused by the polarized charges is opposite to the applied field. Thus the resultant field due to the presence of the insulator is less intense than the case when there is only empty space between the plates. This property of dielectric is called permittivity, ε. For empty space the permittivity is ε0. The relative permittivity is 
Pingback:Electrostatics, Physics 12 … msas – msa
Pingback:capacitance-of-plates-capacitor – msa
Pingback:equi-potential-surfaces and lines … msa – msa