Select the correct answer of the following questions:
1. A water wave moves in two dimensions from the source point and at a far distance the curvature of the wave front becomes plane. As the wave proceeds the energy carried out by the wave.
| (a) decreases | (b) increases | (c) remains constant | (d) it needs some more information |
Explanation: We know that area of the circle is πr2. Therefore, when the radius of the circle increases, its area also increases. Similarly, as the water wave proceeds onward, its covered area increases. So the wave, which carries the energy, now spreads the energy in a larger area. As a consequence the intensity (energy per unit area or energy density) of energy also decreases.
2. When a wave goes from one medium to another medium, which one of the following characteristics of the wave remains constant?
| (a) velocity | (b) frequency | (c) wavelength | (d) phase |
Explanation: Frequency of the wave is the same as the frequency of the source producing the wave. Therefore, it does not change when the wave enters from one medium into the other.
3. When a transverse wave is reflected from the boundary of a denser medium to a rare medium, it undergoes a phase change of:
| (a) 0 | (b) π/2 | (c) π | (d) 2π |
4. If the tension in the string is doubled and its mass per unit length is reduced to half, the speed of transverse wave on it is:
| (a) doubled | (b) halved | (c) constant | (d) one fourth |
Solution: The relation among the tension in the string, the mass per unit length of the string and velocity of the wave produced is given by
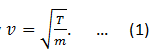
Now if tension is doubled, T = 2T and mass per unit length is halved, m = m/2. Put these values in (1).
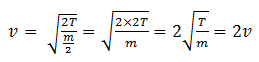
(5) Which one of the following properties is not exhibited by the longitudinal waves?
| (a) reflection | (b) interference | (c) diffraction | (d) polarization |
Explanation: See comprehensive question 9, chapter 9.
6. A sounding source and a listener are both at rest relative to each other. If wind blows from the listener towards the source, then which one of the following of sound will change?
| (a) frequency | (b) speed | (c) both frequency and speed | (d) wavelength |
7. Which one of the following factors has no effect on the speed of the sound in a gas?
| (a) humidity | (b) pressure | (c) temperature | (d) density |
Explanation: See question 6 in comprehensive questions.
8. When sound waves travel from air to water which of these remains constant?
| (a) velocity | (b) frequency | (c) wavelength | (d) all the above |
9. There is no net transfer of energy by particles of medium in
| (a) longitudinal wave | (b) transverse wave | (c) progressive wave | (d) stationary wave |
Explanation: Energy cannot be transferred in case of stationary waves because at the node point, the particles of the medium are stationary. The standing (stationary) medium particle does not transfer the wave energy to the next particle of the medium.
10. Which one of the following could be the frequency of ultraviolet radiation?
| (a) 1.0 * 106 Hz | (b) 1.0 * 109 Hz | (c) 1.0 * 1012 Hz | (d) 1.0 * 1015 Hz |
Explanation: UV radiations are electromagnetic radiations. They fall in the frequency range of 8 * 1014 Hz to 3 * 1016 Hz.
11. When a stationary wave is formed then its frequency is:
| (a) same as that of the individual waves | (b) twice that of the individual waves | (c) half that of the individual waves | &rad;2 that of the individual waves |
12. Which of the following changes at an anti-node in a stationary wave?
| (a) density only | (b) pressure only | (c) both pressure and density | (d) neither pressure nor density |
13. A sound source is moving towards a stationary listener with 1/10 of the speed of the sound. The ratio of apparent to real frequency is:

Solution: The apparent frequency f’ is given by the relation
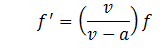
[See question 9 (1).]
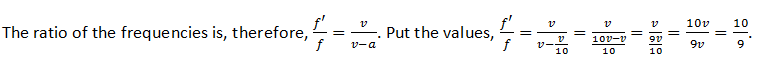

Pingback:Physics 11 (New Course) – msa
Pingback:Numerical Problem 10, Waves, Physics 11 … msa – msa
Pingback:Numerical Problem 1, Waves, Physics 11 … msa – msa